What Causes Pain?
Pain may have many causes and different types:
For example:
Back pain with or without leg pain, Neck pain with or without arm pain. – Also treating spine arthritis resulting in pain limitations of range of motion and walking.
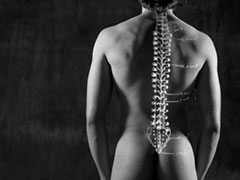
Chronic back pain is often felt in the lower back, but can also extend into your legs or feet. It can also start in the neck and radiates down to the arms. A number of spinal diseases or injuries can trigger chronic back and leg pain, including degenerative disc disease, disc herniation, failed back surgery syndrome, epidural fibrosis, and arachnoiditis. Symptoms range from mild discomfort to completely disabling. You may feel a sharp or knife-like pain, a burning or electric sensation sensation, or a dull muscular ache. Affected areas may feel tender or sore to the touch and the pain may increase with movement or coughing or sneezing..
Painful Neuropathy – Painful neuropathy is a neurological disorder where you experience severe chronic pain due to nerve damage to the nerves that connect the spinal cord to the body and help the brain communicate with skin, muscles, and internal organs. Damage may be a result of nutritional imbalances, alcoholism, toxins, infections, autoimmunity, and illnesses, such as kidney failure or cancer, and nerve trauma. Symptoms include stabbing or sharp pain, burning and numbness in the hands or feet.
Cancer Pain – Cancer most of the time causes pain. Cancer pain may be caused by surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy; scar tissue resulting from surgery or cancer treatment; or a tumor that has grown into – or crowded out – organs, nerves, or other parts of the body. Cancer pain usually falls into one of two categories:
- Nociceptive Pain – Caused by tissue damage by any reason including trauma, described as sharp, aching, or throbbing.
- Neuropathic Pain – Caused by actual nerve damage; described as a burning, ice cold, heavy sensation, or numbness.
We also treat Abdominal or Pelvic Pain – That can result from variety of reasons including pancreatitis or endometriosis.
Nerve Pain – Due to shingles or trigeminal neuralgia that can cause face pain. Occipital neuralgia that can cause headaches
Headache – Including migraine and cluster headache.
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) – CRPS, also known as reflex sympathetic dystrophy or causalgia, is a chronic pain condition that most often affects the arms, legs, hands, or feet. CRPS usually develops in a limb after an injury (such as a broken bone) or surgery that may have involved nerve damage. The overriding symptom is extreme pain, frequently described as burning. Other symptoms can include sensitivity to touch, skin changes, swelling, weakness, and decreased function of the hand/foot. Early diagnosis and treatment is crucial to prevent tissue damage.
How is Pain Treated?
A variety of pain management techniques are available to our specialists at The Woodlands Pain Institute to help ease your suffering. The choice of treatment depends on your specific needs: the type and severity of pain, as well as how you respond to different pain treatments. Not all treatments may be applicable to your pain.
Treatments includes but not limited to :
Non-Drug Treatments – Techniques such as relaxation, biofeedback, imagery, hypnosis, acupuncture, exercise, and counseling help many people use less pain medication.
Physical Therapy – Physical therapy builds or reconditions muscles – allowing you to move more normally and with less pain. We may recommend passive physical therapy, such as massage and applying heat/cold, or active treatments, such as exercise.
Psychological Therapy – Chronic pain can result in stress that impacts you, your relationships, and your body. Psychologists are available to work with you on relaxation techniques, coping and self-monitoring skills.
Nonopioid Oral Medications (Pills) – If non-drug techniques have not had the desired effect, we will try non- opioid oral medications. They include mild pain relievers such as acetaminophen and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen, muscle relaxers and others.
Opioids – If non-opioid medications are not effective in controlling your pain, the next step is opioids, such as Tramadol or Hydrocodone. Opioids are similar to natural substances (endorphins) produced by the body to control pain.
Neurostimulators – Neurostimlators are surgically implanted in the body to send mild electrical impulses to the spine, that you ,mostly, don’t feel it and blocks the pain signal traveling to the brain. Unlike some surgeries, you can try a neurostimulators ( also known as neuromodulation ) in advance of surgery to be sure it will be effective. It is also reversible; we can turn it off or remove it and they are all MRI compatible with our MRI magnet and similar.
Intrathecal drug delivery system: A Pain pump implanted for pain or stiffness using an innovative technique with micro dosing (minute amounts ) to improve function under the skin and eliminate the need for medications.
Corrective Surgery – In doing tests, such as MRI or CT scans, to look for the cause of your pain, we may discover a problem that needs to be corrected by surgery, we refer to surgery ONLY as the last resort.
Therapeutic Nerve Blocks – Therapeutic nerve blocks are local anesthetic and/or steroid injections given at the origin of pain. Nerve blocks usually provide temporary pain relief. If your pain is not managed after multiple injections, we may consider other treatments.
Nerve ablation – With neveroablation, the nerves that serve as pain pathways to the brain are destroyed (usually with heat) without any effect on any other nerves.
Kyphoplsty: Is cement injected in the broken spine that function as an internal cast and provides immediate relief, without open surgery or stitches, only a band-aid.
So many other modalities we use for all sorts of pain.

